Understanding User Authentication: 3 Basics You Should Know
One of the most important aspects of website authentication focuses on the user and human-to-computer interactions. As a result, user authentication is important to understand when creating or improving your website’s login procedure.
Whether you’re looking to amp up your internal security or provide a better user experience to the people registering for an account on your site, it’s important to know how user authentication fits into the equation.
That’s why we’ve created this guide to help organizations understand:
What user authentication is and why it’s important
How many types of user authentication exist
Ways organizations can improve their user authentication
With more understanding, your organization will be able to look into more convenient login processes like allowing users to log in using their social media or email accounts. Additionally, when you gain a full picture of the different types of user authentication, you’ll see that passwords aren’t the only option for your organization.
Let’s dive right into the first section.
1. Understanding User Authentication and Why It’s Important
What Is User Authentication?
As we mentioned earlier, user authentication covers all the human-to-computer interactions that require the user to log in to access certain information.
When a user registers for an account, the user must create an ID and key that will allow them to access their account later on. Generally, a username and password are used as the ID and key, but the credentials can include other forms of keys as well.
How Are Users Authenticated?
In order to gain access, users must prove to the website that they are who they say they are. The ID and key are enough to confirm the user’s identity, which will allow the system to authorize the user.
It’s important to note that authorization is what dictates what users are able to see and do when they log in.
To put it simply, user authentication has three tasks:
Manage the connection between the human (user) and the website’s server (computer).
Verify users’ identities.
Approve (or decline) the authentication so the system can move to authorizing the user.
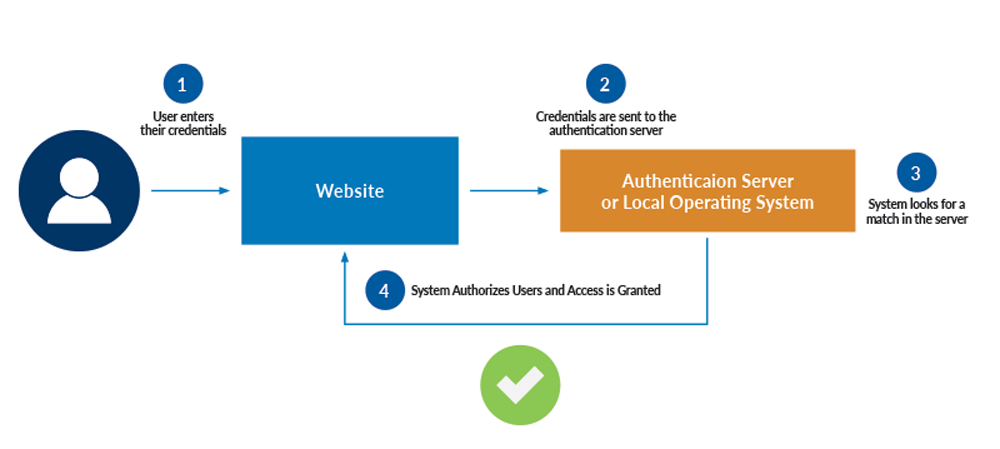
This image details the process:
As you can see, users will input their credentials on the website’s login form. That information is then sent to the authentication server where the information is compared with all the user credentials on file. When a match is found, the system will authorize users and grant them access to their accounts.
If a match isn’t found, users will be prompted to re-enter their credentials and try again. The entire process takes just a couple of seconds to complete.
Why Is Understanding User Authentication Important?
Fully understanding user authentication is crucial because it’s the process that keeps unauthorized users from gaining access to sensitive information.
Authentication ensures that User A only has access to the information they need and can’t see the sensitive information of User B.
When your user authentication isn’t secure, cybercriminals can trick the system and gain access, taking whatever information they want.
Websites like Yahoo, Equifax, and Adobe that were victim to data breaches are prime examples of what happens when organizations fail to secure their websites.
Bottom Line: User authentication ensures that only authorized users are gaining access to sensitive information. Without a secure authentication process, your organization could be at risk.
2. Types of User Authentication
In order for a user to confirm their identity, the individual must provide a piece of information that only the user and the server knows. This information is called an authentication factor, and there are three types:
Knowledge factors. Factors the user must know in order to log in are considered a knowledge factor. This can be anything from a username, password, or pin number. The challenge with these factors is that they can be weak in terms of security because they can be shared or guessed.
Possession factors. Anything that the user must have in order to log in is known as a possession factor. One-time password tokens, key fobs, ID cards, and physical tokens are all considered possession factors.
Inheritance factors. Using a person’s biological characteristics is known as an inheritance factor. Any biometric authentication process, such as fingerprint scanning and face recognition, would fall into this category.
The way users can verify their identity can be divided into two categories: password and passwordless options. Let’s take a closer look at each.
Password Login Systems
Most users are familiar with passwords. In fact, passwords have been the tried-and-true method for user authentication since the beginning of the internet.
The user authentication process with passwords, generally, looks like this:
When you land on the page, you’ll be asked to enter your username and password.
Your credentials are sent to the website’s server and compared with the information they have on file.
When a match is found, you’ll be able to enter your account.
While a password may be sufficient to secure simple accounts like social media profiles or other online communities, the truth is that many of us store more sensitive information online. To top it all off, users are managing an average of 25 accounts—and that’s just in our personal lives.
That’s a lot of passwords to keep track of! As a result, many users have chosen convenience over security. Instead of creating strong passwords, most users use a simple arrangement of letters, numbers, and symbols because it’s easier to remember.
What’s more, 54% of users use 5 or fewer different passwords across their accounts.
All these factors (and many more!) lead to poor security. Hackers are able to guess a user’s credentials or use computer technology to run through possible combinations until they find a match.
Let’s face it: passwords have a lot of weaknesses and aren’t sufficient in protecting our information. Luckily, they aren’t the only way users can verify their identities.
Passwordless Login Systems
To put it simply, a passwordless login system is an authentication method that doesn’t require a password. In the past couple of years, these types of authentication methods have become more popular—and you’ve probably experienced a few.
There are several different types of passwordless login, but in this article, will cover two of the most common types:
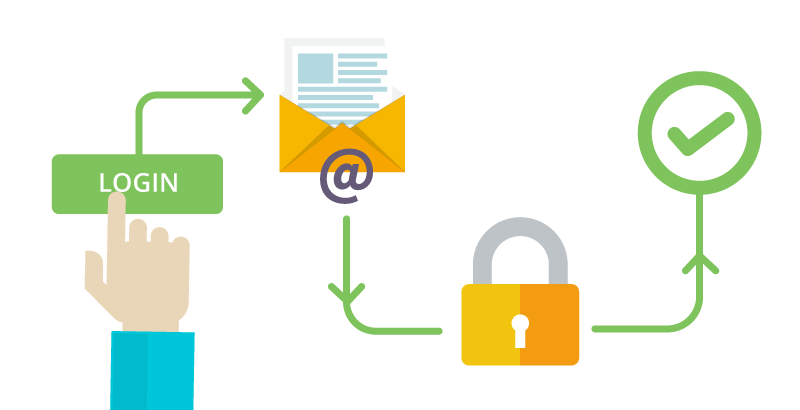
Email Authentication
Email authentication is one of the most universal passwordless authentication types because anyone with an email account can use this method.
With this method, users can create an account, log in, and make payments with just a click of a button!
Biometrics
Fingerprint and iris scanning, face recognition, and other types of verification through biological characteristics all fall under the category of biometrics.
This authentication type is often considered one of the most secure options for users because everyone’s biological characteristics are unique and can’t be easily duplicated.
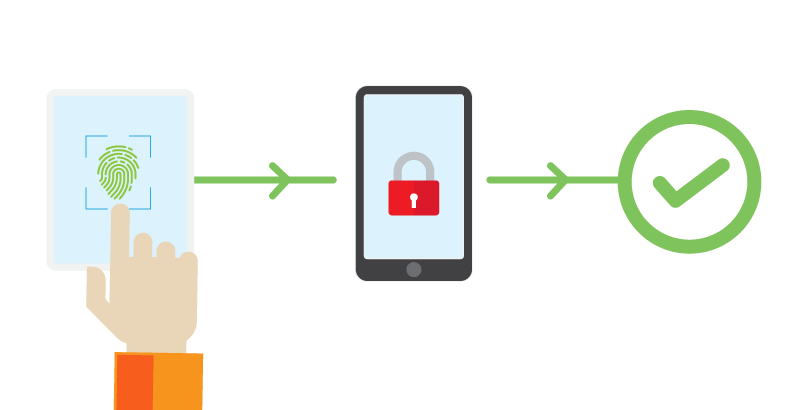
Another benefit of biometrics is that the user experience is convenient and easy to understand. For example, with fingerprint authentication, the user only needs to complete one step—the rest is the system’s responsibility:
The user presses his finger on the scanner and waits for the system to grant him access.
Behind the scenes, the system compares the fingerprint scanned with the original print on file.
If the two match the system grants the user access.
Despite its many benefits, biometric authentication does have a few downsides. First, recent studies have shown that duplicating a person’s fingerprints is easier than we think.
By creating a master print with characteristics that are common in most fingerprints, hackers are able to trick the scanners 65% of the time. Additionally, high-quality images can be used to trick face recognition login systems.
Another concern is that if someone does steal your fingerprints, you’d never be able to safely use that method of authentication again.
Lastly, biometrics isn’t accessible to everyone; the user needs a special device that can scan fingerprints, irises, or faces.
Bottom Line: With several different ways to verify your account, it’s important to look at the pros and cons of each one and determine which option fits your organization’s needs.
3. Ways Organizations Can Improve Their User Authentication
Now that you understand how user authentication works and have discovered some of the many ways users can authenticate their identities, it’s time to see how you can improve your process.
Encourage Users to Create Stronger Passwords
If your organization only decides to do one thing to improve your user authentication, it should be to encourage users to create better passwords. With stronger credentials, your user’s information has a better chance of staying protected.
Organizations should not only encourage users to create stronger passwords but also enforce these guidelines internally so that employees maintain secure accounts as well.
When improving your passwords, here are a few things to keep in mind:
Longer passwords are more secure. Security experts suggest that you create passwords with a minimum of 8 characters, but we recommend that you create passwords closer to 12 characters long.
Passwords should have a mix of characters. Passwords with a random combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols are harder to crack.
Users should avoid using formulas when generating passwords. The truth is that formulas make it easy for hackers to guess your password and can offer users a false sense of security.
For even more password tips, check out this image:
To help encourage users to create stronger passwords, your organization can scan all newly generated passwords against a list of already compromised passwords to prevent people from using weak credentials.
Implement SSO Authentication
If you’re not familiar with the term SSO authentication, it’s a process that lets you stay logged on even when you move to a different domain. This system is ideal for organizations that have various products and services located on different websites.
Google is a great example of how this system works. When a user logs into their Gmail account, they’ll have access to all of Google’s services—YouTube, Google Analytics, Google Drive, etc.—without needing to sign in again.
When SSO authentication is used, users will be able to drastically cut down the number of accounts they have to manage. With fewer passwords to remember, users can focus on creating stronger credentials.
Use Passwordless Login
If you agree with many security experts that believe passwords are obsolete, it’s time to implement a passwordless login option.
Bottom Line: Encouraging users to make stronger passwords, using systems that consolidate the number of accounts a user has to manage, and implementing passwordless login are all great ways you can improve the security and user experience of your login process.